What is a Foot Fault in Volleyball

While playing volleyball, players need to understand that they are not allowed to just land their feet anywhere while serving and attacking the ball. Otherwise, they end up committing the foot fault.
What is a foot fault in volleyball? A server commits a foot fault when they put their foot over the service line. Volleyball servers must keep both of their feet behind the service line while hitting the ball. And attackers commit foot fault when they have their whole feet beyond the centerline.
Is Foot Fault Only Also Applicable to Servers?
Not only servers but attackers can also commit foot faults in volleyball. However, all the faults while attacking are generalized as “attack hit fault.”
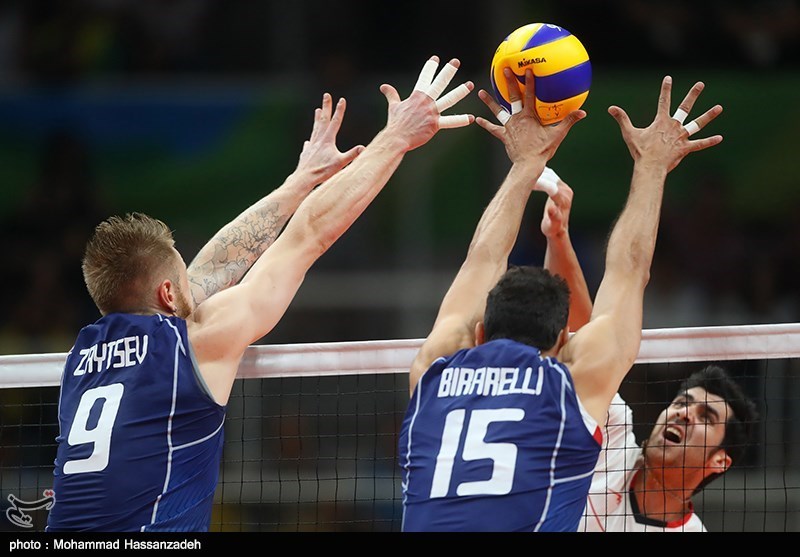
Just like the servers are not allowed to touch the service line, frontcourt attackers are also not allowed to cross the centerline of the volleyball court. If they do it, they end up committing the foot fault, or as it is commonly known, a centerline foot fault violation.
However, it must be kept in mind that attackers must land their complete foot beyond the centerline in order to commit the violations. If only a part of their foot is touching/crossing the centerline, it is not considered a foot fault.
In case of servers, they cannot even touch the service line while serving the ball.
Likewise, backcourt attackers or Defensive Specialists are also not allowed to touch the attack line, which is present 3 meters away from the center of the court. If they do it, the opposite team gets a score due to an attacker committing a foot fault.
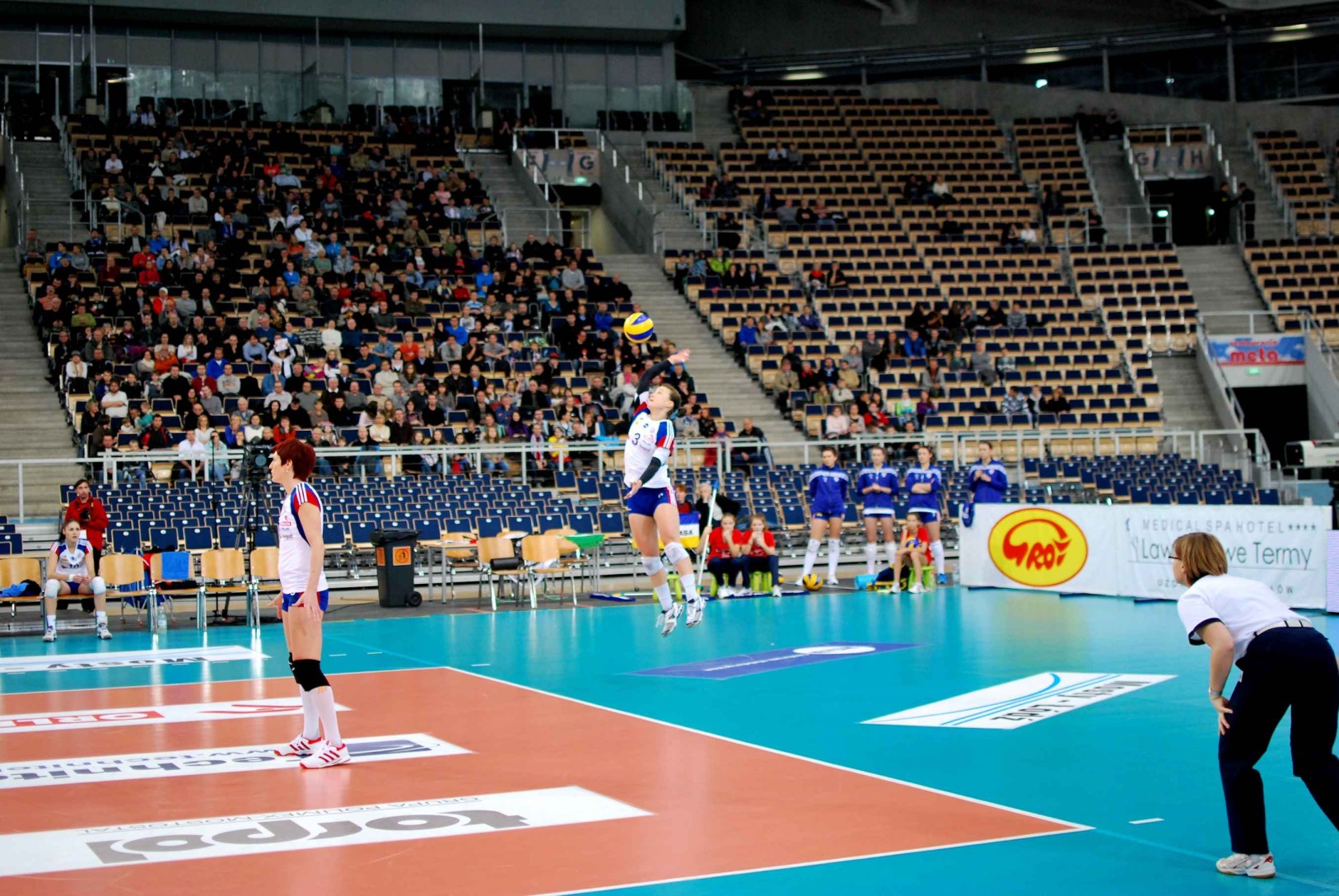
Below you can see a server committing a foot fault
Here you can see frontrow attacker committing a foot fault aka centerlike violation.
How to Avoid Foot Fault in Volleyball?
- For servers, jumping is an important part of the whole serve. So you need to make a perfect jump in order to avoid a foot fault. Servers need to jump before the baseline; otherwise, they commit a foot fault. Remember that a server can always hit the volleyball by coming into the court’s airspace, but they are just not allowed to touch the line with their foot. So always put the ball in the air before the service line, and hit in by coming in court’s airspace.
- For attackers who are seeking to smash the ball legally without committing foot fault, they need to keep the weight of the body on their back while smashing the ball instead of putting too much weight on the front side of the body, particularly the chest.
If you put the unnecessary weight on your chest while smashing the ball, you are likely to commit the center line foot fault violation, as stopping the feet right after landing is extremely difficult this way.
- For backrow attackers, the weight of the body plays a crucial role just like for front row attackers. The back-row attackers also need to avoid putting weight on the chest. Proper bending practices while smashing the ball is one of the ways to avoid foot fault violations during the game.
Is Foot Fault a Common Error in Volleyball
Amateur servers will often find themselves committing foot fault errors, but it is something that is easy to avoid, espcecaiily for servers. So, professional servers usually serve the ball easily without the foot’s fault.
However, attackers (both the front and back row” committing a foot fault is a very common error. Many a times, players are unable to carry their momentum and end up crossing the lines to commit foot fault.
What Does the Volleyball Rulebook Say About Foot Fault?
FIVB rules are simple, yet detailed, about the foot fault
For attackers, FIVB states,
To touch the opponent’s court with a foot (feet) are permitted, provided that some part of the penetrating foot (feet) remains either in contact with or directly above the center line, and this action does not interfere with the opponent’s play.
1.3.3, D11 (22) FIVB
And Also this one;
(Player will be at fault if ) A player’s foot (feet) penetrates completely into the opponent’s court.
11.2.2.2, D11 (22) FIVB
At his/her take-off, the player’s foot (feet) must neither have touched nor crossed over the attack line.
1.3.4 FIVB
For Servers, FIVB Rules say;
At the moment of the service hit or take-off for a jump service, the server must not touch the court (the end line included) or the floor outside the service zone. After the hit, he/she may step or land outside the service zone, or inside the court.
1.4.2, 29.2.1.4, D11(22), D12 (4) FIVB
What Happens After a Foot Fault?
When a team commits a foot fault, the opposing team gets a score and also an opportunity to serve the ball. The official term for the change of service is known as sideout.
Which Volleyball Referee Makes a Call for Foot Fault Violation?
The volleyball foot fault is usually called by the first referee sitting at the elevated position. However, second referees also monitor whether the server is touching the service line or not, which helps the primary referee to make the decision.
Most of the time, the second referee will see the foot fault committed by the attackers. While the lines judge will see any foot fault committed by the server.
As the foot fault margin can get extremely small at times, the decision can also get referred to the challenge referee, who sees the reply to decide if the foot fault violation is committed or not.
The opposing team can also challenge the foot fault call.
What Does Umpire Signal After the Foot Fault Violation?
Umpire usually points out downward toward the service line to indicate a foot fault.
Line Judge makes this sign for foot fault
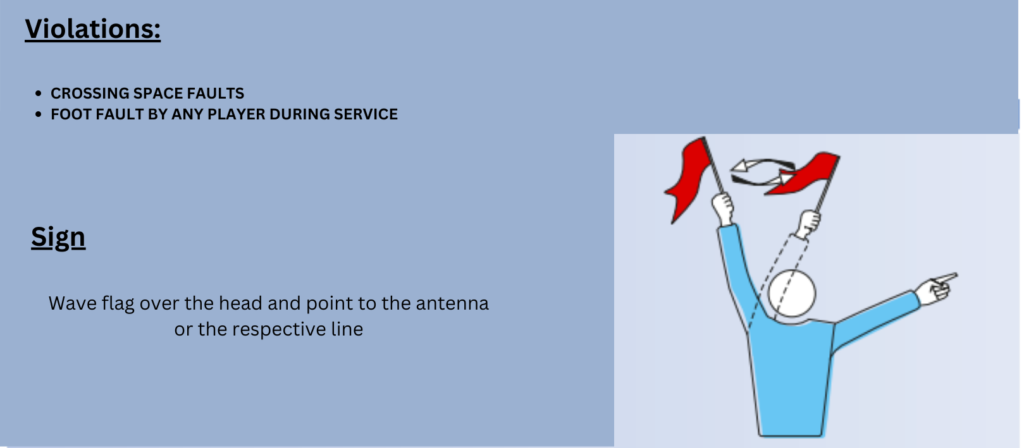
1st Referee makes this signal for backrow foot fault

1st Referee makes this sign when attackers make centerline foot fault violation

Final Thoughts
Volleyball rules are designed to make the game competitive and enjoyable.
Keeping the foot in the dedicated areas is to make sure that no player steps in the area in which they are not allowed to enter.
While foot fault during service is avoidable since it is just the start of the rally, centerline fault and back row attack foot fault are still committed by many players in regular games.

Ahmed is the founder of Ball and Net Sports, a platform where he writes about volleyball.
As a professional volleyball player who has participated in various national and international level volleyball competitions, he loves to teach other volleyball enthusiasts about the game.
He is now a professional volleyball coach who organizes volleyball camps and social events for talent hunting for top volleyball teams.
As a volleyball talent-hunting specialist, he loves to teach people how they can make their game better in the fast-paced volleyball environment where it is extremely difficult to get quality content free of cost.